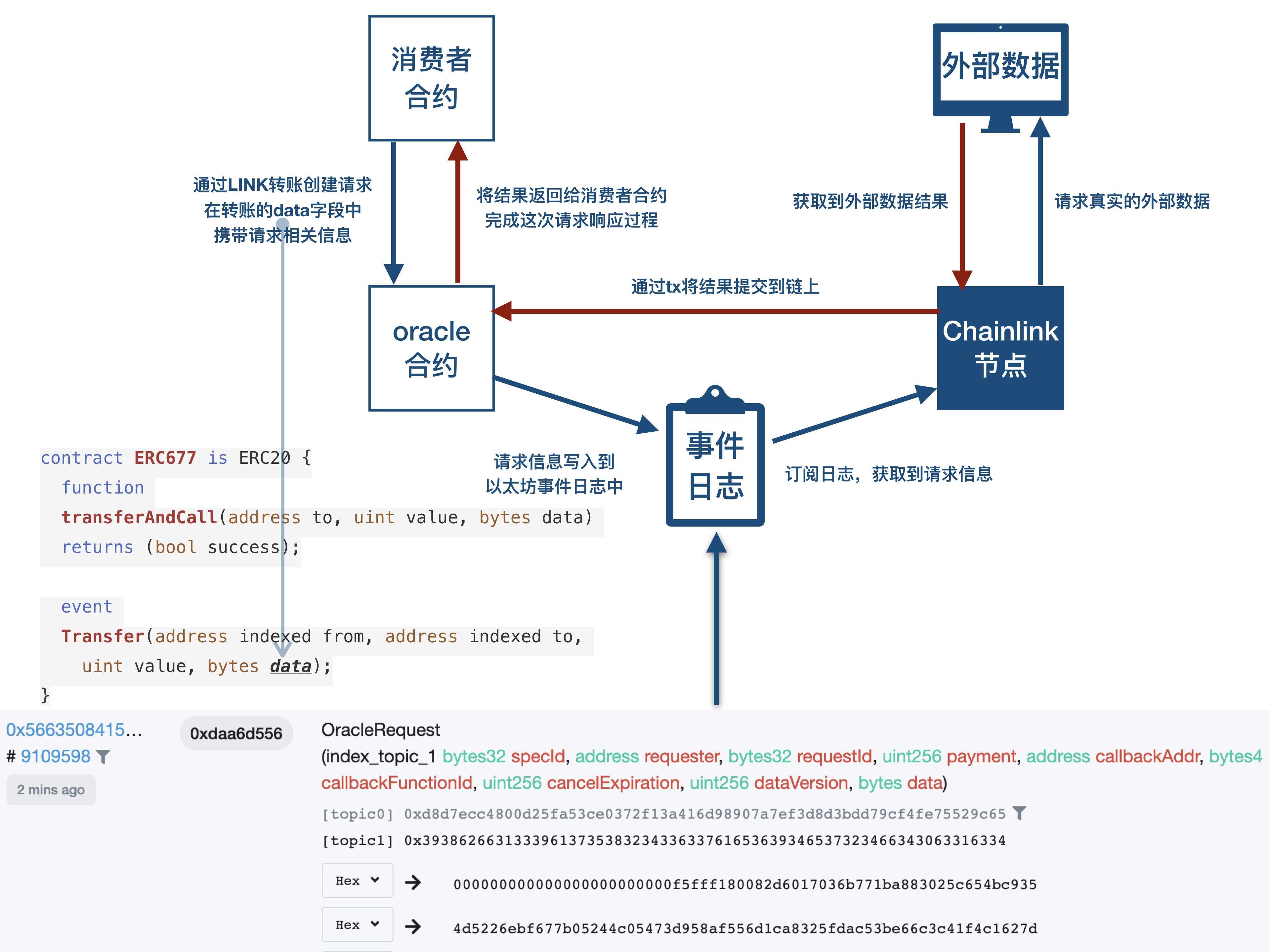
作者:团长 Part1:https://bihu.com/article/1630155434 Part2:https://bihu.com/article/1099786509
我们以Chainlink提供的 function requestEthereumPrice(address _oracle, string _jobId)
public
onlyOwner
{
Chainlink.Request memory req = buildChainlinkRequest(stringToBytes32(_jobId), this, this.fulfillEthereumPrice.selector);
req.add("get", "https://min-api.cryptocompare.com/data/price?fsym=ETH&tsyms=USD");
req.add("path", "USD");
req.addInt("times", 100);
sendChainlinkRequestTo(_oracle, req, ORACLE_PAYMENT);
}它所实现的功能就是从指定的API(cryptocompare)获取ETH/USD的交易价格。函数传入的参数是指定的oracle地址和jobId。将一些列的请求参数组好后,调用 /**
* @notice 向指定的oracle地址创建一个请求
* @dev 创建并存储一个请求ID, 增加本地的nonce值, 并使用`transferAndCall` 方法发送LINK,
* 创建到目标oracle合约地址的请求
* 发出 ChainlinkRequested 事件.
* @param _oracle 发送请求至的oracle地址
* @param _req 完成初始化的Chainlink请求
* @param _payment 请求发送的LINK数量
* @return 请求 ID
*/
function sendChainlinkRequestTo(address _oracle, Chainlink.Request memory _req, uint256 _payment)
internal
returns (bytes32 requestId)
{
requestId = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(this, requests));
_req.nonce = requests;
pendingRequests[requestId] = _oracle;
emit ChainlinkRequested(requestId);
require(link.transferAndCall(_oracle, _payment, encodeRequest(_req)), "unable to transferAndCall to oracle");
requests += 1;
return requestId;
}其中 /**
* @dev 将token和额外数据一起转移给一个合约地址
* @param _to 转移到的目的地址
* @param _value 转移数量
* @param _data 传递给接收合约的额外数据
*/
function transferAndCall(address _to, uint _value, bytes _data)
public
returns (bool success)
{
super.transfer(_to, _value);
Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value, _data);
if (isContract(_to)) {
contractFallback(_to, _value, _data);
}
return true;
}其中的 event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint value, bytes data); 将这次转账的详细信息(发送方、接收方、金额、数据)记录到日志中。 Oracle合约在收到转账之后,会触发 event OracleRequest(
bytes32 indexed specId,
address requester,
bytes32 requestId,
uint256 payment,
address callbackAddr,
bytes4 callbackFunctionId,
uint256 cancelExpiration,
uint256 dataVersion,
bytes data
);这个日志会在oracle合约的日志中找到,如图中下方所示。链下的节点会订阅该主题的日志,在获取到记录的日志信息之后,节点会解析出请求的具体信息,通过网络的API调用,获取到请求的结果。之后通过提交事务的方式,调用Oracle合约中的 /**
* @notice 由Chainlink节点调用来完成请求
* @dev 提交的参数必须是`oracleRequest`方法所记录的哈希参数
* 将会调用回调地址的回调函数,`require`检查时不会报错,以便节点可以获得报酬
* @param _requestId 请求ID必须与请求者所匹配
* @param _payment 为Oracle发放付款金额 (以wei为单位)
* @param _callbackAddress 完成方法的回调地址
* @param _callbackFunctionId 完成方法的回调函数
* @param _expiration 请求者可以取消之前节点应响应的到期时间
* @param _data 返回给消费者合约的数据
* @return 外部调用成功的状态值
*/
function fulfillOracleRequest(
bytes32 _requestId,
uint256 _payment,
address _callbackAddress,
bytes4 _callbackFunctionId,
uint256 _expiration,
bytes32 _data
)
external
onlyAuthorizedNode
isValidRequest(_requestId)
returns (bool)
{
bytes32 paramsHash = keccak256(
abi.encodePacked(
_payment,
_callbackAddress,
_callbackFunctionId,
_expiration
)
);
require(commitments[_requestId] == paramsHash, "Params do not match request ID");
withdrawableTokens = withdrawableTokens.add(_payment);
delete commitments[_requestId];
require(gasleft() >= MINIMUM_CONSUMER_GAS_LIMIT, "Must provide consumer enough gas");
return _callbackAddress.call(_callbackFunctionId, _requestId, _data); // solhint-disable-line avoid-low-level-calls
}这个方法会在进行一系列的检验之后,会将结果通过之前记录的回调地址与回调函数,返回给消费者合约: _callbackAddress.call(_callbackFunctionId, _requestId, _data); 这样一次请求就全部完成了。 总结 本文从预言机的概念开始,通过一个简单的获取ETH价格的例子,讲解了请求/响应模式的Chainlink预言机的基本过程,希望对你理解预言机与Chainlink的运行原理有所帮助。 (完结) (文中代码仅用于说明文章内容,请勿直接用于生产环境) Chainlink官方渠道QQ群: 6135525 微博:https://weibo.com/chainlinkofficial 币乎:https://bihu.com/people/1869894547 合作联系:[email protected] GitHub:https://github.com/smartcontractkit/chainlink Gitter:https://gitter.im/smartcontractkit-chainlink/Lobby Twitter:https://twitter.com/chainlinkofficial Telegram:https://t.me/chainlinkofficial —- 编译者/作者:Chainlink 玩币族申明:玩币族作为开放的资讯翻译/分享平台,所提供的所有资讯仅代表作者个人观点,与玩币族平台立场无关,且不构成任何投资理财建议。文章版权归原作者所有。 |
Chainlink预言机基本原理(三)
2019-12-26 Chainlink 来源:区块链网络
LOADING...
相关阅读:
- 宣传全民光盘CFCC珍惜粮食公链落地应用2020-10-29
- 游侠区块链10月28日分析:比特币高点13850完美预期后市偏空2020-10-28
- 掌控币圈风云:10.28晚间ETH多单入场2020-10-28
- 领峰环球:外汇市场、外汇交易以及外汇交易商各指的是什么?2020-10-28
- 王赋辽:10.28德指·恒指·纳指·道指晚评分析及策略2020-10-28